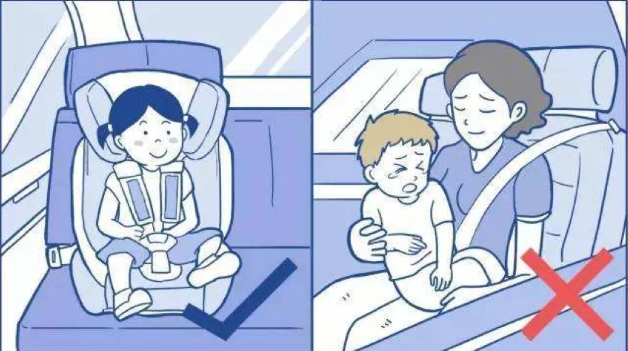
Globally, traffic accidents are one of the leading causes of unintentional injury deaths among children. Each year, tens of thousands of children lose their lives or are injured in road crashes—a heartbreaking statistic. Child safety seats, designed specifically to protect children, are undeniably critical. This blog explores the necessity of child safety seats from a global perspective, supported by data and real-world examples.
Introduction
Children are far more vulnerable in traffic accidents than adults. Their developing bodies, with less robust bones and muscles, make them prone to severe injuries during collisions. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 180,000 children die annually in traffic accidents worldwide, many of which are preventable. Child safety seats, as an effective protective measure, can significantly reduce child fatalities and injuries in crashes.
The Role of Child Safety Seats
Child safety seats are designed to provide protection tailored to a child’s physiology. Unlike adults, children have larger heads relative to their bodies and underdeveloped neck muscles, making their heads and necks particularly susceptible to injury in a crash. Child safety seats use specialized restraint systems and cushioning materials to disperse impact forces, safeguarding the head, neck, and spine.
Research shows that correctly used child safety seats can reduce the risk of death by 71% for infants (under 1 year) and by 54% for toddlers (ages 1-4). These figures underscore the profound impact of child safety seats in protecting young lives.
Global Regulations and Standards
To ensure the quality and safety of child safety seats, international regulations and standards have been established. The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) has set widely recognized standards, including ECE R44/04 and ECE R129 (i-Size). These standards regulate the design, materials, and testing of child safety seats to ensure effective protection during collisions.
Different countries have also implemented their own regulations. For example:
- United States: All 50 states mandate the use of child safety seats, with specific requirements varying by state.
- European Union: All member states must comply with ECE R44/04 or ECE R129 standards.
- China: The 2015 national standard, Restraint Systems for Child Occupants of Motor Vehicles, regulates the production and use of child safety seats.
Global Data Support
The global child traffic fatality rate is closely linked to the usage rate of child safety seats. According to the International Road Safety Organization, countries with higher child safety seat usage rates have significantly lower child traffic fatality rates. For instance, Sweden, one of the highest adopters of child safety seats, has among the lowest child traffic death rates globally.
Key data points include:
- Over 180,000 children die in traffic accidents worldwide annually (WHO, 2018).
- In the U.S., 794 children under 12 died in traffic accidents in 2017, with nearly 40% unrestrained (NHTSA, 2019).
- In China, over 18,000 children under 14 were injured or killed in traffic accidents in 2019.
These statistics highlight the critical importance of child safety seats in reducing child traffic fatalities.
Case Studies
Positive Example
In 2018, a 2-year-old child in the UK survived a severe traffic accident unscathed. The vehicle lost control on a highway and crashed into a guardrail, leaving adult passengers seriously injured. However, the child, properly secured in a safety seat, sustained only minor scratches. This case vividly illustrates the life-saving potential of child safety seats.
Negative Example
In 2019, a 4-year-old child in China, seated in the front passenger seat without a safety seat, was critically injured. When the vehicle braked suddenly, the child was propelled into the windshield, suffering severe head trauma. This tragedy underscores the dire consequences of neglecting child safety seats.
Parental Education and Awareness
Parents play a pivotal role in the effective use of child safety seats. Raising awareness and equipping parents with the knowledge to correctly select and install safety seats are key to reducing child traffic injuries. Recommendations include:
- Attending educational programs on child safety seats to learn proper selection and installation.
- Regularly inspecting safety seat installations to ensure they are secure.
- Teaching children to remain calm in the car to avoid distracting the driver.
Governments and organizations should also intensify efforts to promote awareness through media campaigns and community initiatives.
Conclusion
Child safety seats are indispensable tools for protecting young lives, a fact supported by global data and real-world cases. Governments, automakers, and parents must collaborate to strengthen regulations, improve compliance, and increase the adoption of child safety seats, creating a safer travel environment for children worldwide.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Status Report on Road Safety. 2018.
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Child Safety Seat Guidelines. 2019.
- United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). ECE R44/04 and ECE R129 Standards. 2015.
- China National Standardization Administration. Restraint Systems for Child Occupants of Motor Vehicles. GB 27887-2011.
- International Road Safety Organization. Global Child Safety Seat Usage Survey. 2020.